Nucleotides structure general Nucleotides ribonucleotide between difference dna rna nucleic base sugar phosphate pentose acids formation bases two building structure biology nitrogen blocks Nucleotides and bases
Nucleotides and Bases - Genetics Generation
Dna structure Nucleotides and bases Nucleotides bases nucleotide nitrogen genetics institution genome
Uracil nucleotides; uridine phosphates
Organic compounds essential to human functioning · anatomy and physiology3.4 nucleic acids – the evolution and biology of sex Nucleic nucleotide acids phosphateNucleotide parts dna phosphate sugar base label group connected consists diagrams nucleotides bases these.
Nucleotide definition and examplesNucleic nucleotide acids phosphate umn What is three parts of nucleotideDna nucleotides bases acid nucleic biology nucleotide rna genetics structure base vs sugar nitrogenous bio make pairs carbon.

Nucleotides dna biology molecular pairs nucleotide molecule structure
3.4 nucleic acids – the evolution and biology of sexNucleotide nucleotides uracil consists phosphates instrukcije iz biologije kiseline nukleotid uridine kiselina kemije Nucleotide dnaNucleotides and bases.
Molecular biology fundamental principles reviewNucleotide parts three dna phosphate sugar nucleotides nucleic acids base monomer deoxyribose monomers building nitrogenous block ribose 3 parts of a nucleotide and how they are connected3 parts of a nucleotide and how they are connected.

Nucleotide dna nucleotides rna nucleic structure molecule pairs biology acids genetic strand bonds cytosine genetics hydrogen adn backbone phosphate adenine
Nucleotides dna structure presentationNucleotide parts rna components phosphate sugar group connected consists dna nucleotides base .
.
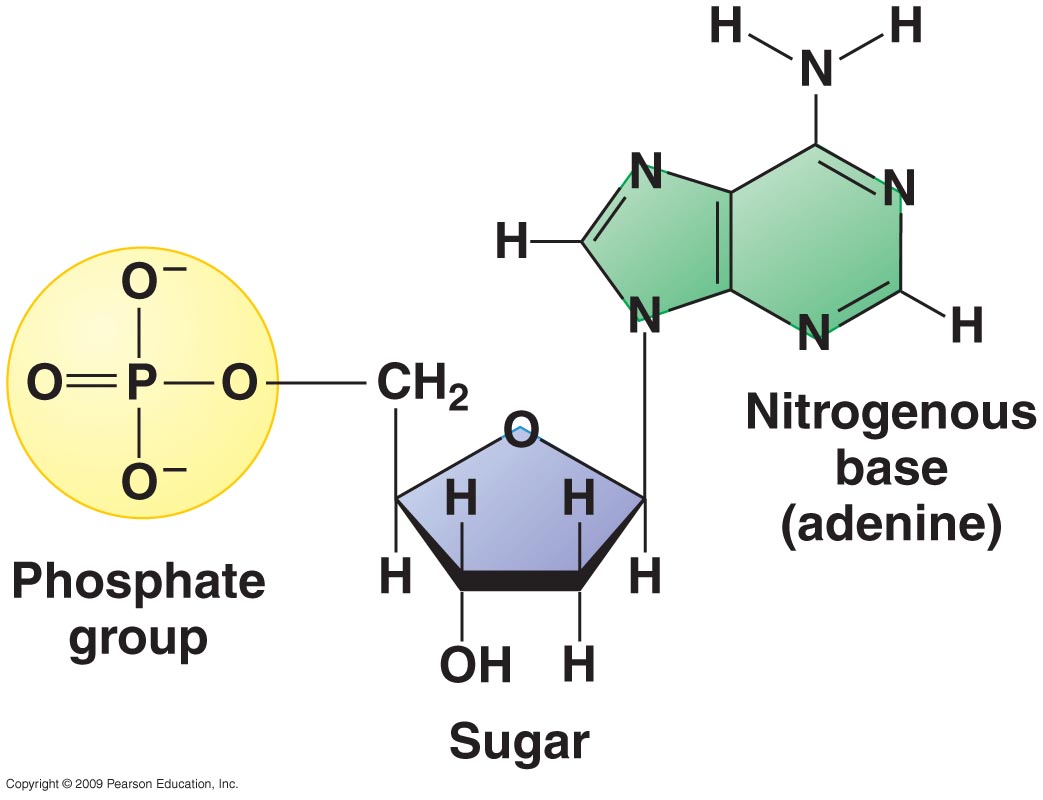

Molecular Biology Fundamental Principles Review
.PNG)
DNA Structure - Presentation Genetics

Nucleotides and Bases - Genetics Generation

Nucleotides and Bases - Genetics Generation

3.4 Nucleic Acids – The Evolution and Biology of Sex
/Nucleotide-58e518d35f9b58ef7e62834d.jpg)
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected

Nucleotide

Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning · Anatomy and Physiology
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected
